
- 630
- 0
THERANOVA…… A breakthrough science in dialysis treatment
The loss of kidney function in patients with kidney failure causes accumulation of solutes termed as uremic toxins, which have immense negative effect on patient health. The uremic syndrome is attributed to the progressive retention of a large number of compounds, which are unable to be excreted by the less functional kidneys or non-functional kidneys.
These compounds are called uremic retention solutes or uremic toxins, which interact negatively with biological functions of the body. These toxins can be grouped into small water soluble molecules, middle molecules, and protein-bound solutes.
Although smaller molecules can be effectively removed by conventional dialysis, but it is quite difficult to clear the middle molecules by the conventional HD process.
Middle molecules can be further subdivided into two groups on the basis of their molecular mass: conventional middle molecules and larger middle molecules. Β2-microglobulin is considered the standard representative of a middle molecule whereas large middle molecules include free Ig light chains.
Larger middle molecules are associated with inflammation, cardiovascular events, and other dialysis-related comorbidities in patients with cardiovascular disease, mineral and bone disorders, and infectious diseases.
Highly porous membranes, as those featured in high-flux dialyzers, allow some middle molecules to pass through the membrane, but even these membranes do not readily clear larger solutes. Larger middle molecules need to be removed either by convection or through the use of highly permeable membranes.
To avail expanded dialysis service, contact- +91 98746 04925
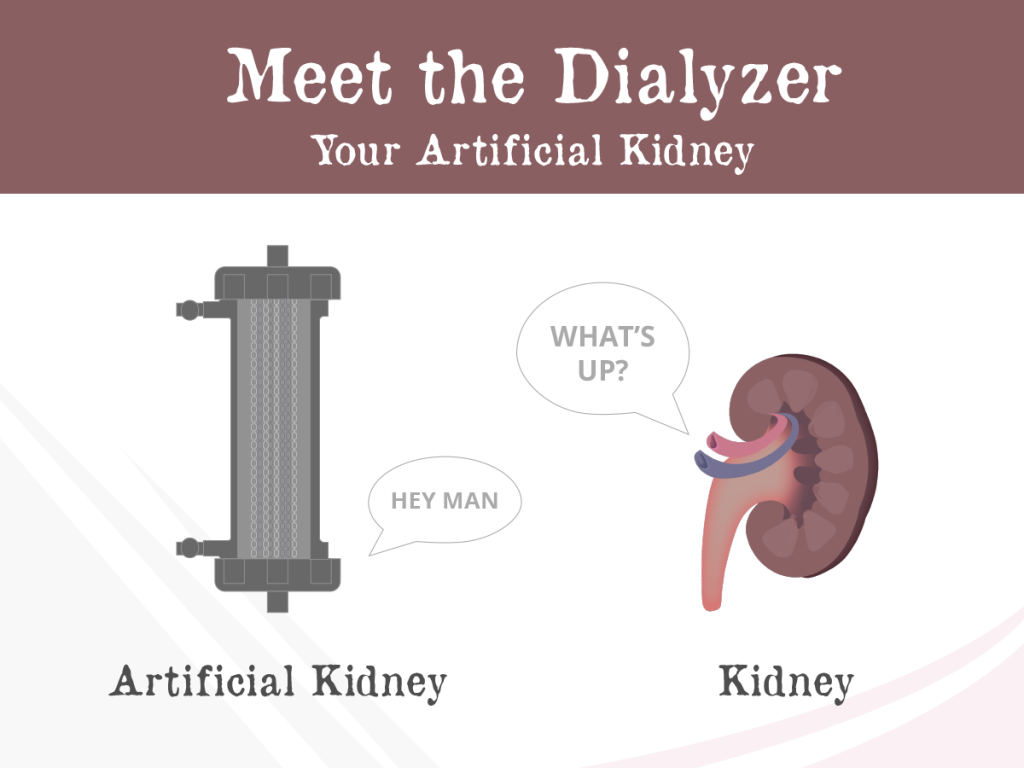
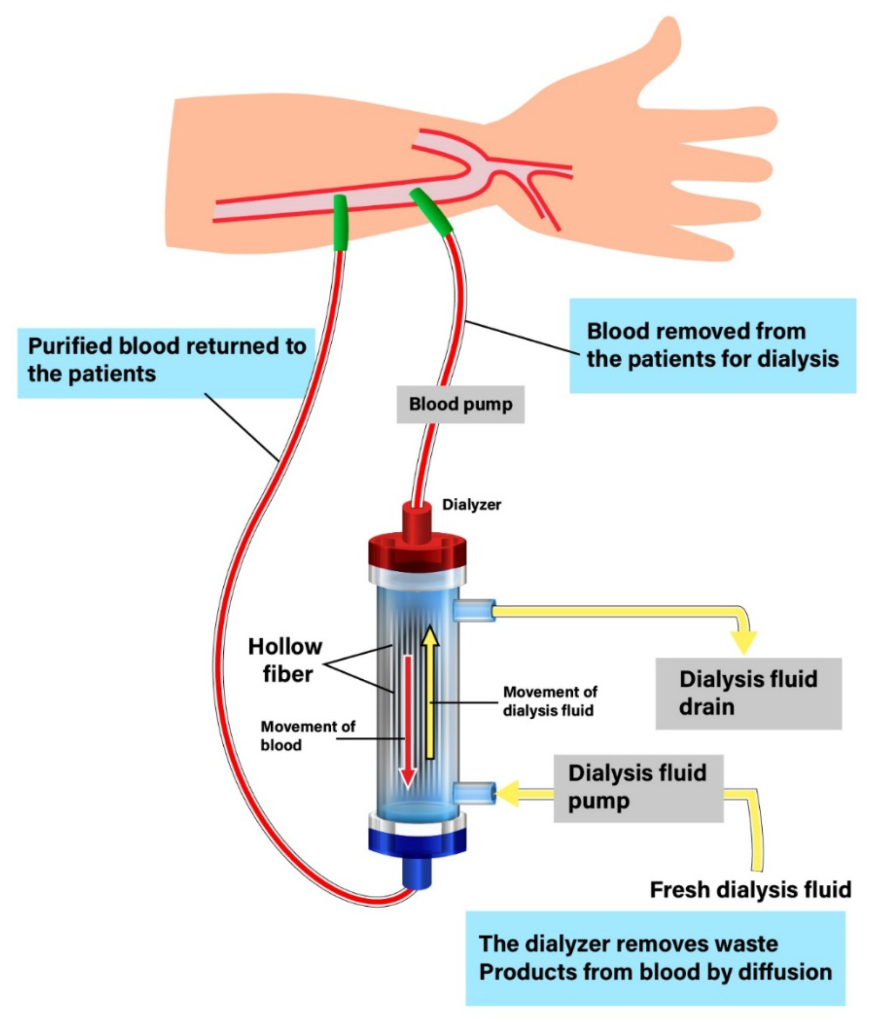
A dialyzer can also be considered as an “artificial kidney.” Its function is to remove the excess wastes and fluid from the blood when an individual’s kidneys can no longer perform effectively. Dialyzers are made of thin, fibrous material with, a medium cut-off membrane, which combines high permeability and uremic toxin selectivity.
Factors that influence the choice of dialyzer:
1. The membrane material of the dialyzer.
2. Biocompatibility of dialyzer and dialysis membrane.
3. The clearance capability of the dialyzer.
4. The ultrafiltration potential of the dialyzer.
5. The dialyzer’s area and the blood chamber’s volume.
The accumulation of solutes in patients with chronic kidney disease may be associated with complications resulting in poorer outcomes, including higher morbidity and mortality. These uremic retention solutes, also known as uremic toxins, range widely in size from small molecules to middle molecules. Larger middle molecules, are associated with comorbid conditions that are common in dialysis patients such as inflammation and cardiovascular events.
What is HDx dialysis?
Expanded hemodialysis (HDx) therapy is a novel treatment concept for hemodialysis patients, which involves the usage of membrane technology that has a high retention onset for better solute (uremic toxins) clearance in the upper middle molecular range.
Theranova dialyser is designed for expanded hemodialysis (HDx) therapy.
What is Theranova dialyzer?
The Theranova Dialyzer is recommended for patients with kidney failure who are prescribed or dependent on hemodialysis. It provides an expanded solute removal option that increases the removal of various large middle molecules which cannot be removed through other form of dialysis.
WHY THERANOVA 400…… Reason and Utility
1. Theranova is a hollow-fiber, single-use dialyzer, with improved removal of large proteins, as well as selective maintenance of essential proteins such as albumin.
2. Theranova 400 dialyzer, through its innovative design, combines the functional features of enhanced permeability, increased selectivity, controlled retention, and improved internal filtration, into a single dialyzer.
3. This is a specialized dialysis treatment called “expanded Hemodialysis”, where diffusion & convection are integrated inside a hollow fiber dialyzer, equipped with a medium cut-off membrane.
4. Theranova 400 enables removal of small, conventional middle molecules as well as large middle molecule uremic toxins.
5. Expanded hemodialysis therapy through Theranova 400 helps superior of larger middle molecules that comprise putative uremic solutes, than conventional high-flux dialyzer. At the same time maintains good level of serum albumin.
6. Reduced loss of protein helps in maintaining health balance and thus promotes better immunity.
Eligibility for Theranova400
1. Patients who are clinically stable without acute medical events for 30 days prior.
2. Receiving HD with a high-flux dialyzer for at least 3 months prior.
3. Patient having stable functioning vascular access.
4. Patients with chronic liver disease, paraprotein-associated disease, hepatitis, HIV, bleeding disorders, active cancer, and monoclonal plasma diseases are not suitable for expanded HD.8
Conclusion
Optimal removal of uremic solutes has been a goal of HD since its inception. New technologies, enhancing the clearance of middle molecules while limiting the loss of important proteins, such as albumin, have an important role in improving the health of patients on dialysis.
It is possible that expanded HD may potentially demonstrate improved mortality with long-term treatment because of better clearance of larger middle molecules. Theranova 400 membrane, will be a real paradigm shifts in the provision of kidney care as envisioned by the Nephrocare India Pvt Ltd. Hence, with a goal of good renal care for all, we have successfully introduced the expanded hemodialysis at Nephrocare through THERANOVA 400. And we are on continuous process of upgradation, so as to offer the best possible treatment for our patients.
To avail expanded dialysis service, contact- +91 98746 04925
What kind of patient would be eligible for Theranova? Let us know in the comment section
Comment
Check Your EGFR
***We Promise, no spam!






