- 1015
- 0
Life-Saving First Aid: How to Act Fast in Critical Situations
Accidents and emergencies can occur unexpectedly at any place or time. Understanding basic first aid can be the difference between life and death in such situations. First aid involves giving immediate care to someone who is injured or unwell until professional medical assistance is available. By learning essential first-aid skills, we equip ourselves to respond quickly and efficiently during emergencies. Here is a guide to some crucial first-aid techniques that everyone should be familiar with.
Understanding the Basics
First aid encompasses a range of practices aimed at preserving life, preventing further harm, and promoting recovery. The key principles include:
- Preserve Life: The main goal is to keep the person alive and stabilize their condition until professional help arrives.
- Prevent Further Harm: Avoiding further injuries and preventing the situation from worsening is crucial. This can involve moving a person away from danger or ensuring they are breathing properly.
- Promote Recovery: This involves providing comfort and taking steps that help in the person’s recovery process.
The Heimlich Maneuver for Choking
- Choking occurs when an object blocks the airway, preventing the person from breathing. The Heimlich Maneuver is an effective technique to dislodge the obstruction.
How to Perform the Heimlich Maneuver:
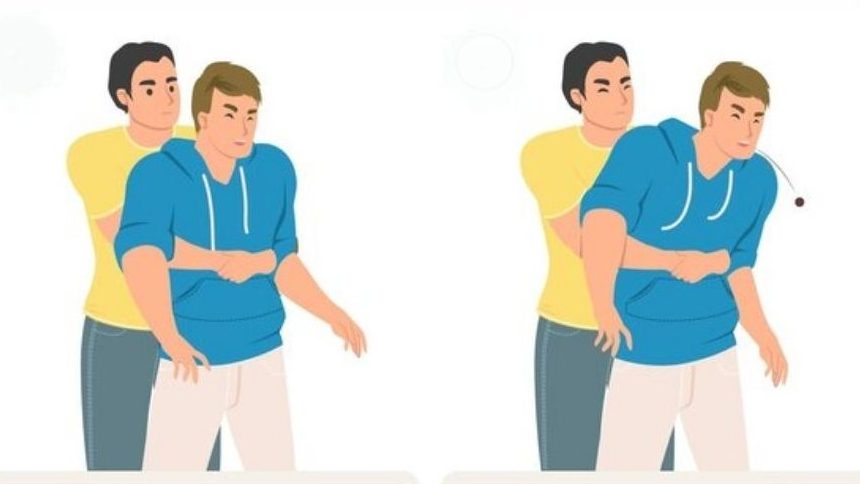
- Position yourself behind the individual and encircle their waist with your arms.
- Form a fist with one hand and position it just above the belly button, below the ribcage.
- Hold your fist with your other hand and perform rapid, upward thrusts into the abdomen.
- Continue until the object is dislodged, or the person can breathe or cough again.
Controlling Bleeding
- Severe bleeding can lead to shock or even death if not controlled quickly. Knowing how to manage bleeding is crucial in first aid.
Steps to Control Bleeding:
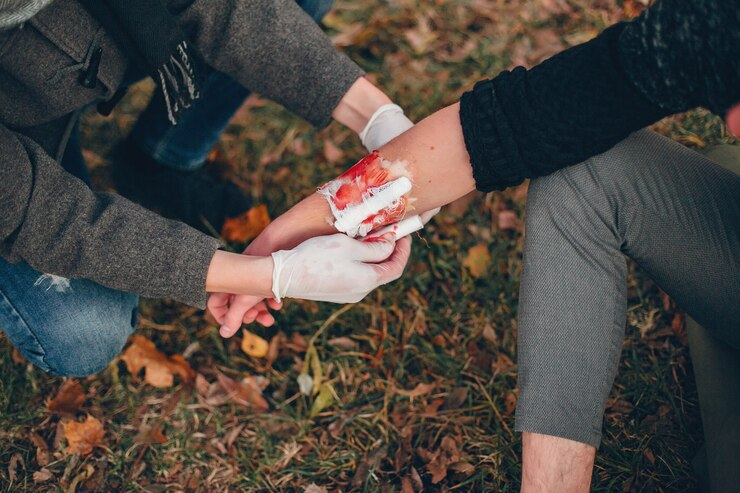

- Apply Pressure: Place a clean cloth or bandage over the wound and press down firmly. This helps to control bleeding by allowing the blood to clot.
- Elevate the Limb: If the injury is on an arm or leg, raise the limb above the heart level to slow down blood flow to the wounded area.
- Use a Tourniquet: If direct pressure does not stop the bleeding, a tourniquet may be used as a last option. Apply it 2-3 inches above the wound on the limb and tighten it until the bleeding ceases.
Managing Burns
- Burns can result from heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation. Rapid first aid can diminish damage and prevent complications.
First Aid for Burns:
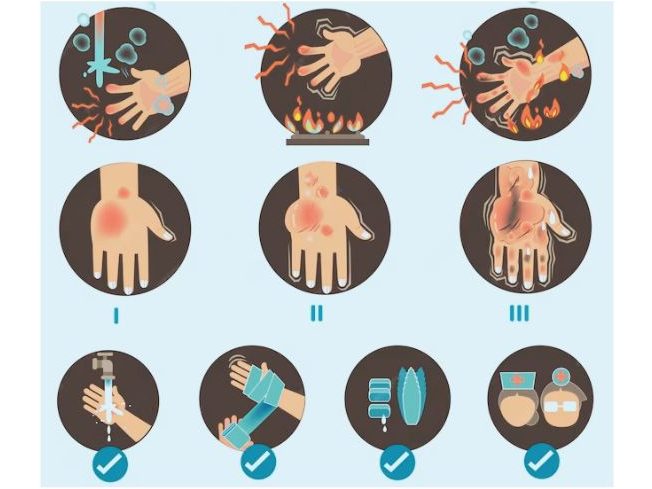
- Cool the Burn: Run cool (not icy) water over the burned area for 10 minutes to alleviate pain and minimize swelling.
- Shield the Burn: Use a sterile, non-stick bandage or a clean piece of cloth to cover the burn and safeguard the skin.
- Uses of Ice and Creams: Refrain from using ice, butter, locally available cream, or ointments on the burn, as they may aggravate the injury and harm the skin further.
- Measures to prevent infection in the future.
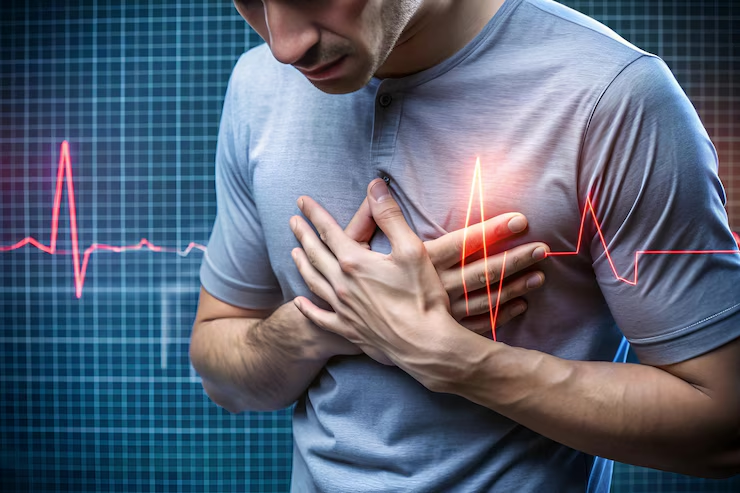
Recognizing and Responding to a Heart Attack
- A heart attack occurs when the blood supply to a part of the heart is blocked. Identifying the symptoms early can save a life.
Symptoms of a Heart Attack:
- A sensation of pain or discomfort in the chest, frequently characterized by pressure, tightness, or a feeling of fullness.
- Discomfort or pain that may extend to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or abdomen.
- Symptoms include difficulty breathing, nausea, dizziness, or experiencing cold sweats.

First Aid Response:
- Contact emergency services right away.
- Encourage the person to sit down and remain calm.
- Can given S/L sorbitate for angina pain
- If the person develops cardiac arrest start CPR.
Dealing with Fractures and Sprains
- Fractures and sprains are common wounds that involve careful handling to avoid further damage.
First Aid for Fractures and Sprains:
- Keep the Area Stable: Ensure the injured limb remains stationary. If needed, use a splint or sling to prevent movement.
- Use Cold Therapy: Applying ice can help decrease swelling and alleviate pain. Make sure to wrap the ice pack in a cloth before placing it on the injured area.
- Get Professional Help: It’s important to consult a healthcare provider for potential fractures or serious sprains.
To receive emergency care, please get in touch with our Nephrocare team.
Conclusion
First aid isn’t just about addressing injuries; it’s about being ready to respond in emergencies. By acquiring and practicing these essential skills, you can have a meaningful impact when it really counts. Encourage those around you to learn first aid – you never know when it could be crucial.
Comment
Check Your EGFR
***We Promise, no spam!






